News Roundup

Infrastructure group awarded £1.2bn Lower Thames Crossing contract
Balfour Beatty has been awarded a £1.2bn contract by National Highways to deliver the ‘Roads North of the Thames’ package of works for the proposed Lower Thames Crossing. The crossing will create a new connection under the River Thames to increase capacity and ease congestion in the South of England.
The contract includes the design and delivery of more than 10 miles of new highways, connecting the M25 at Junction 29 and the A13 with the Lower Thames Crossing tunnel at Tilbury, Essex, and will see it deliver 49 structures, including bridges and major viaducts. It will utilise modular construction techniques to build the structures offsite in a controlled factory environment, reducing carbon emissions by minimising the number of lorry movements and material deliveries – supporting the company’s commitment to going Beyond Net Zero Carbon by 2040, as well as National Highways’ low carbon targets for the project.
Battery energy storage systems site marks the launch of a new energy ecosystem
The installation of two E-STOR battery energy storage systems, made by Connected Energy from second-life Renault batteries, at a site in Nottingham marks the launch of an energy ecosystem described as ‘next era energy management’. Nottingham City Council’s Eastcroft depot, located just outside the city centre, will demonstrate how a fleet depot can intelligently manage the energy demands caused by vehicle electrification. Home to a 200-strong fleet; the depot includes 40 vehicle-to-grid (V2G) bi-directional chargers with three solar arrays and Connected Energy’s two 300kW E-STOR energy storage systems supporting the charging demands.
The energy ecosystem will be a blueprint for how premises across the country facing extreme energy challenges from physical supply restrictions, rural locations or legacy buildings can install EV chargers and increase their energy consumption, while managing their power demands. Its installation is a key part of Nottingham’s ambition to become the first carbon-neutral city in the country by 2028.
Bentley Systems announces the retirement of founder Keith Bentley
Founder Keith Bentley has stepped down as chief technology officer of Bentley Systems and assumed the role of technology advisor through to his anticipated retirement later in the year. He will continue thereafter on Bentley Systems’ board of directors. His successor as chief technology officer is Julien Moutte. In addition, chief investment officer, David Hollister has retired. He has been succeeded as chief financial officer by Werner Andre.
CEO Greg Bentley said: “It is practically unique for any mature software company to have had, for its lifetime, a chief inventor who has also been its chief evangelist, both for the work of its engineer users and developers. Bentley Systems was founded in 1984 to commercialise Keith Bentley’s software for infrastructure engineering, and Keith’s contributions to the substance and articulation of our work have never slowed down.”
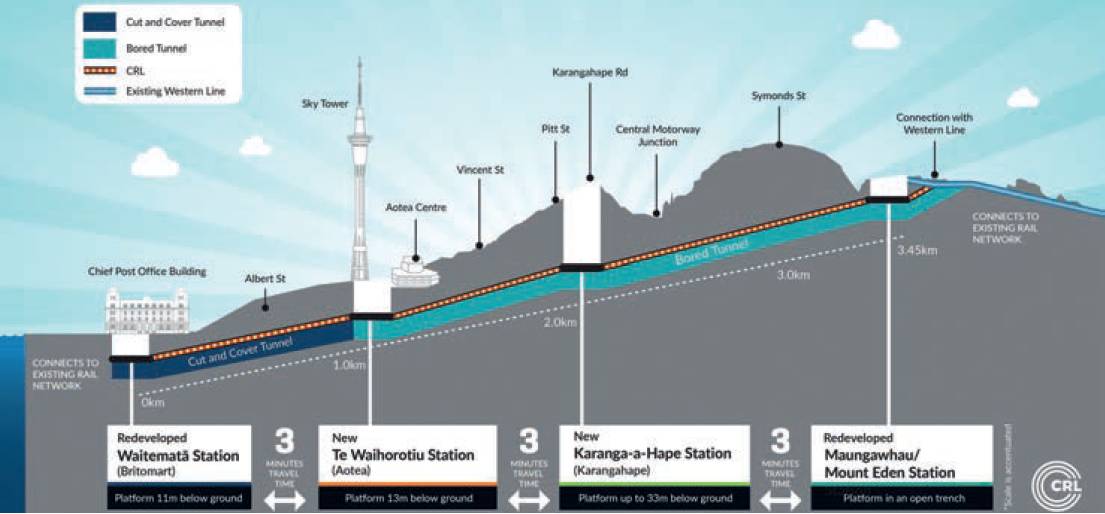
Auckland’s first underground rail line is under construction
The City Rail Link, the largest transport infrastructure project ever to be undertaken in New Zealand, completed its tunnelling was completed in September when the TBM, Dame Whina Cooper, broke through at Te Waihorotiu Station (Aotea) station. The team have moved on to the next phase of the project, fitting out the tunnels.
The CRL is a 3.45km twin-tunnel underground rail link up to 42m below the city centre transforming the downtown Waitemat Station (Britomart) into a two-way through-station that better connects the city’s rail network. It includes a redeveloped Maungawhau Station, where the CRL connects with the North Auckland (Western Line) and new underground stations – one mid-town at Wellesley and Victoria Streets called Te Waihorotiu Station and Karanga-a-Hape Station just off Karangahape Road with entrances at both Mercury Lane and Beresford Square.
Once completed, the NZ$5.49bn project will allow the rail network to at least double rail capacity, helping the notoriously traffic-heavy country to help citizens with their travel plans.

An iconic 16-span viaduct in central Scotland is returned to its former glory
An iconic 16-arch viaduct that straddles the River Avon on the West Lothian and Falkirk border has been restored thanks to renovations funded by National Highways’ Historical Railways Estate.
The £2m programme included masonry repairs, waterproofing and the installation of 19 bat bricks, six bat tubes and two bat boxes, took 18 months to complete and ensures that the structure, built in the 1850s, will be preserved for many generations to come.
Indonesian government to commence work on the country’s planned new capital
Indonesia is set to begin construction of apartments in its planned new capital, Nusantara, for thousands of civil servants costing approximately $2.7bn. The country announced in 2019 its plan to move its capital city from Jakarta to the forested area in Indonesian Borneo because it is sinking due to a lack of water access and the subsequent well digging to counteract this which is leading the underground to compact and sink. It is predicted that by 2050 around a quarter of Jakarta will be underwater
Authorities have already started building basic infrastructure in the area and the aim is to start relocating some government administration and civil servants in 2024. The overall project is estimated to cost $32 billion. It is hoped the plans will help provide equality to the country’s economy.

Image courtesy of HS2.
HS2 reveals the design for the last of seven key Chiltern Tunnel structures
HS2 has revealed the final designs for the North Portal of the Chiltern Tunnel – the last of seven key structures for the high-speed rail project’s longest tunnels.
Once construction is complete, the seven ‘Key Design Elements’ will be the only parts of the tunnel visible to the local community.
Alongside the North Portal, which will be near South Heath in Buckinghamshire, they include the South Portal, near the M25, and headhouses above the ventilation and emergency access shafts, which are mostly designed to resemble agricultural buildings.
The design work has been completed by HS2’s main works contractor, Align JV – made up of Sir Robert McAlpine, Bouygues Travaux Publics, and VolkerFitzpatrick, working with its design partners Jacobs, RendelIngerop and LDA Design, and its architect Grimshaw.
Delays to HS2 announced
The UK government has announced delays to the construction of HS2, the country’s new high-speed train line. The Birmingham to Crewe leg will be delayed by two years to cut costs, while initial services between Old Oak Common in west London’s suburbs and Birmingham Curzon Street will be prioritised as a cost-saving measure amid high inflation. The latter change would see services not stopping in Euston until 2035 at the earliest, with transport secretary Mark Harper citing ‘significant inflationary pressure’ as a reason for the delay to linking up HS2 with Euston.
The track was initially designed to run between London and Birmingham, where it would then split into two – going towards Crewe and Manchester – to be completed in 2034 and 2041 – and also to Leeds. At an estimated cost of £32bn in 2012, the figure had doubled before any construction had started, three years later. Roll on another five years, in 2020, estimations of £106bn led the UK government to scrap the Leeds route to reduce costs down to around £72- £98bn.
Europe’s longest rail tunnel is under construction
As part of the new Trans-European Transport Network, new and upgraded transport links have been built all over Europe – nine in total. This includes the Scandinavian-Mediterranean Corridor which runs from Finland to Malta. However, to complete the Mediterranean Corridor from east to west between Spain and Hungary, engineering work is needed to create a huge hole through a mountain in the Alps to form the Mount Cenis Base Tunnel between Lyon and Turin.
It will become the world’s longest single rail tunnel at 57.5km when finished.
Managed and constructed by Tunnel Euralpin Lyon Turin, it is co-owned by the French and Italian governments. The whole line is set to cost around $27bn, with the tunnel costing $9bn and is due to be completed by 2032.
University of Oxford to co-lead £8.7m grant for an energy demand observatory and laboratory
The University of Oxford, alongside University College London, is to lead on an £8.7m research project to establish an Energy Demand Observatory and Laboratory (EDOL) in the UK. The five-year programme, funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC, part of UK Research and Innovation) and working with the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, will establish a national energy data platform to help facilitate the transition to net-zero carbon emissions.
If the UK is to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, domestic energy will have to stop using natural gas and transition to a low carbon system. However there is currently very little information on how this will impact patterns of energy usage, and whether this will overlap with other changes to the UK’s energy system, including the increased uptake of electric cars and heat pumps. The EDOL will address this by providing a high-resolution data resource that will track energy use in real households, enabling us to understand how, why, and when domestic activity is impacting energy demand and associated carbon emissions.
African infrastructure has been given a $253.7m boost from $12bn climate fund
The Green Climate Fund, a $12bn initiative funded by developed nations, has made a $253.7m investment to back global warming-resilient infrastructure in Africa. It will serve as an anchor investment in the Infrastructure Climate Resilient Fund, managed by Nigeria-based Africa Finance Corp.’s asset management unit, AFC Capital Partners. This new funding will initially target projects in 19 countries with the first expected to be power lines which can withstand violent weather, renewable energy plants and ports which can adapt to rising sea levels.
In brief:
- Bentley Systems has acquired EasyPower, a power systems engineering software company. The company has also announced a collaboration initiative with WSB to lead civil infrastructure owners and contractors to adopt and use infrastructure digital twins, as well as entered into a strategic agreement with Worldsensing to strategically accelerate the adoption of infrastructure IoT.
- Fugro and Petrobras have achieved a major milestone in Brazil’s offshore energy sector by successfully completing the country’s first-ever remote subsea inspection survey.
- A new satellite-based system to detect methane emissions, the Methane alert and response system (MARS) initiative, developed by the European Space Agency and launched at COP27, will scale up global efforts to detect and act on major emissions sources and accelerate the implementation of the Global Methane Pledge. It will be the first Copernicus mission dedicated to monitoring our atmosphere.
- Northumbrian Water has appointed Stantec as a strategic technical partner for asset management period eight to support the delivery of the water company’s resilience and sustainability ambitions.
- Thales plans to hire more than 12,000 new employees in 2023 to support its growth, It includes 1,050 in the UK, 5,500 in France, 600 in Australia, 550 in India and 540 in the US. These new employees will support Thales in its core markets, aerospace, defence and security, and digital identity and security.
- Research by Protrade has revealed the uptake of construction apprenticeships are on the rise again for the first time in six years – 26,100 new apprenticeships started in the sector in 2021-22. The data, however, shows more still needs to be done to improve diversity across the sector – female apprenticeship representation declined slightly.
- Hyperloop developing companies Hardt, Hyperloop One, Hyperloop Transportation Technologies, Nevomo, TransPod, Swisspod Technologies, and Zeleros have joined forces to form ‘The Hyperloop Association’, the first global association within the hyperloop industry.
- Topcon has acquired Digital Construction Works.